Public Private Partnership (PPP, 3P, or P3) is a frequently pronounced term in the field of infrastructure development & contract management. It is a widely adopted model mainly for public service delivery. So, before diving into the concept of public private partnership, it is good to know about public service delivery & the various options available for it.
What is Public Service Delivery?
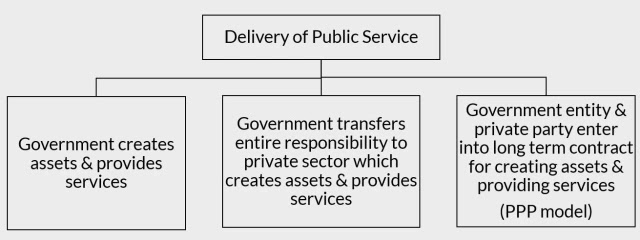
Public service delivery is a mechanism by which public services are delivered to the public by the local, provincial or federal government. Such services may include public education, public health, transportation facilities, irrigation, drinking water, electricity, etc. A set of institutional arrangements are made by the government in order to deliver the goods & services to the citizens. So, the government has duties & rights to deliver public service which is provided by designated officials in the stipulated time frame. A responsive government must be capable to manage the efficient delivery of basic services. There may be the following different modes available for the development of assets & delivery of services.
In the first model of public service delivery mention in the diagram above, government alone develops infrastructures & provides services to people which is quite traditional & straightforward model. Here the revenue generated from taxpayers is also taken by the government itself. Such a model may fail if the government becomes unable to remain active throughout the project cycle. In the second model of public service delivery, government transfers the entire responsibility to the private sector for creating assets & providing services to the people. The drawback here is that the private entity may only adhere to their profitability & may become careless to the quality of public service delivery. So, in order to reduce such drawbacks, we enter into the third model where legal binding occurs between government & private entities for the provision of delivery of public services which is also called public private partnership.
What is Public Private Partnership?
PPP Knowledge Lab defines public private partnership as a long-term contract between a private party and a government entity, for providing a public asset or service, in which the private party bears significant risk and management responsibility and remuneration is linked to performance. This is the latest model & best reliable alternative for infrastructure development in today's market.
What are the advantages of public private partnership for government & end-users?
Improved Service Delivery
By allowing both sectors to give their best, the quality of service delivery gets improved. Also, the private entity is always well aware to earn the most out of it providing the best facilities.
Better economic viability
Using the advantage of the private sector's innovation & technology, PPP can become more economically viable. The involvement of well-experienced sponsors & leaders of the private sector can increase the cost-effectiveness of the project. Due to the flexibility of private sectors, there will be reduced delay resulting in the faster completion of the project.
Inflow of private investment
PPP increases the private investment in public infrastructures & thus allows the government funds to be redirected elsewhere in the community.
Risk sharing
Construction, completion & operational risk associated with any project are shared by private parties thereby reducing the risk of the public sector. Transferring risk to the private sector can reduce the potential cost overrun of government due to unforeseen circumstances.
What are the benefits of public private partnership for the private sector?
Investment opportunity
PPP provides a secure & long-term investment opportunity for the private sector. Also, they are granted to obtain remuneration for the long run. Without PPP, the private entity may not have a chance to work on major capital infrastructure projects.
Resource Mobilization
PPP makes optimum use of technology, people & skills available with a private entity. The expertise of the private sector can be utilized fully allowing them to gain more experience & knowledge in the field.
What are the demerits of Public Private Partnership?
Increased Cost
The production cost may increase as the private sector also demands its profit for accepting risk & investing in the project. The procurement process is more costly in comparison to traditional public procurement. Also, if the PPP goes wrong, it may be very expensive for the taxpayers.
Reduced Control
Since the control gets divided between the government & private entity, there may be reduced control if any one of the party become less responsible. It may be subjected to political exposure as the government sectors also share control over it.
Complex legislation
If any unforeseen issue arises during project execution, there may be the necessity for renegotiation to accommodate the contingencies. Thus, a clear legal framework is crucial.
What types of contracts are done in public private partnership?
There are several contracting models available for public private partnerships based on the type of service to be delivered. The BOOT (Build-Own-Operate-Transfer) model can be taken as an example to best describe the concept. In the BOOT model, there occurs legal binding between private party & government entity where private party builds the facility & owns till the duration of the contract. It also operates the facility & generates revenue from end-users. Since the contract duration is usually of a long time frame, the private party can easily recover its investment during the payback period & earns profit thereafter. At the end of the contract, the facility is handed back to the government. Likewise, there are the following different models available for contracting PPP:
Build-Transfer (BT)
Build-Own-Transfer (BOT)
Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT)
Build-Own-Operate (BOO)
Build-Transfer-Operate (BTO)
Lease-Operate-Transfer (LOT)
Develop-Operate-Transfer (DOT)
Are there any public private partnership examples in Nepal?
The PPP model is widely practiced for hydropower projects in Nepal. There is small-scale initiation for urban development. Some of the national pride projects are also contracted under this model. Public private partnership policy, 2015 has been formulated to promote PPP practice in Nepal. Some of the major projects under PPP are listed below:
Hydropower Sector
Khimti Khola hydropower project
Chilime hydropower project
Bhotekoshi hydropower project
Upper Tamakoshi hydropower project
West Seti hydropower project
Road Sector
Kathmandu Terai fast track
Kathmandu Kulekhani Hetauda tunnel
Airport Sector
Nijagdh international airport
Gautam Buddha international airport

Very fruitful, thank you sir 🙏❤️
ReplyDeleteYou Welcome! 😊
DeleteSir,can you please tell me what is the scope of ppp model
ReplyDelete