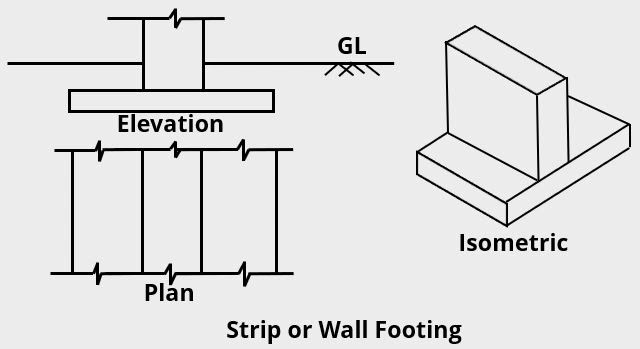
What are the Criteria for Selection of Ideal Bridge Site?
Principles & Techniques of Bioengineering for Civil Engineers
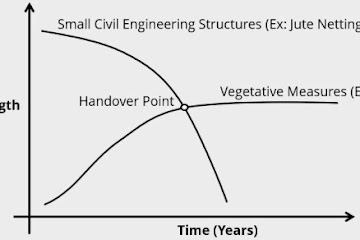
In a broader sense, Bioengineering is the use of life science & engineering to solve human life problems. Here, in this article, we are using the term bioengineering in the context of civil engineering & it basically refers to soil bioengineering. So, Bioengineering can be defined as the use of vegetative measures & small civil engineering structures in order to reduce the shallow seated instability. The living plants or non-living plant materials are used alone or in conjunction with small civil engineering structures for slope stabilization & erosion control. It utilizes locally available resources & is a cost-effective method.
Principles of Bioengineering
Functions of Bioengineering
- Catch
- Armor
- Reinforce
- Anchor
- Support
- Drain
Advantages of Bioengineering
- Immediate slope stabilization & erosion control
- Utilization of locally available resources (local tools, local manpower, local materials)
- It is a cost-effective method
- No need for frequent maintenance
- It also provides an opportunity for wildlife habitat
- It also improves the aesthetic beauty of the site
Commonly Used Techniques of Bioengineering
- Fascine: Bundle of live branches laid in shallow trenches
- Palisade: Woody cuttings planted across the slope.
- Wattling: Fence made out of vegetative materials.
- Bamboo Planting: Planting of bamboo for soil conservation
- Grass Planting: Planting of grass across the slope
- Brush Layering: Layers of woody cuttings planted in line following the contour
- RipRap: Stone pitching with vegetation interplanted between them
- Retaining Wall: Wall built to resist the pressure of earth filling or backing
- Toe Wall
- Breast Wall or Revetment Wall
- Check Dam: Dams constructed across the gullies to retard the flow
- Gabion Wall: Walls made up of gabion wire filled with stones
- Stone Masonry: Masonry construction using stones & mortar
- Jute Netting: Protecting the slope with standard jute mesh
- Rock Netting: Wire mesh of reliable material used to control the rockfall
- Rock Bolting: Reinforcement of rock slope by inserting steel bars
- French Drain: Subsurface drainage channel filled with aggregates
Degree of Static & Kinematic Indeterminacy of Structures
Parts of Research Paper | How to Write a Research Paper?
A research paper is scientific writing that shapes up an idea into words with solid and verifiable evidence. The main goal of a research paper is to assemble different opinions, perspectives, corroboration, and facts on a subject matter from various resources like articles, books, other research papers, interviews and elucidate the details and findings in one's own words. The most popular types of research papers are argumentative papers, analytical papers, definition papers, compare and contrast papers, cause and effect papers, reports, and interpretive papers.
Federal Nepal: Provinces & Local Levels of Nepal
7 States of Nepal
Province No 1
Province No 2: Madhesh Pradesh
Province No 3: Bagmati Pradesh
Province No 4: Gandaki Pradesh
Province No 5: Lumbini Pradesh
Province No 6: Karnali Pradesh
Province No 7: Sudur Pashchim Pradesh
Local Levels of Nepal
National Parks of Nepal | Wildlife Reserve and Conservation Areas
National Parks
- Parsa National Park
- Shukla Phanta National Park
- Banke National Park
- Shivapuri Nagarjun National Park
- Makalu Barun National Park
- Khaptad National Park
- Shey-Phoksundo National Park
- Bardiya National Park
- Rara National Park
- Langtang National Park
- Sagarmatha National Park
- Chitwan National Park
Wildlife Reserve
Hunting Reserve
Dhorpatan Hunting Reserve is the only hunting reserve in Nepal established in 2044 BS with an aim of preserving a representative high altitude ecosystem in west Nepal and allow sports hunting of blue sheep and other game animals.
Conservation Areas
- Krishnasaar Conservation Area
- Api Nanpa Conservation Area
- Gaurishankar Conservation Area
- Manaslu Conservation Area
- Kanchanjunga Conservation Area
- Annapurna Conservation Area
Hydroelectricity in Nepal | Hydropower Projects in Nepal
Tourism & Its Importance in Nepal
Tourism in Nepal
Importance of tourism in Nepal
The importance of tourism comes to light since it brings in lots of advantages with it to any host country. It promotes the country's name around the globe. It can be a great source of income for a country. Switzerland, France, Italy, Spain, and many other countries today are counted as flourished nations and the main reason behind this is the development of the tourism industry. Nepal each year gets a lot of visits and is in the path of tourism development by pre-planning events and activities to allure tourists. Below are a few points for the importance of tourism in Nepal.
- Economic growth: For a developing country like Nepal, the tourism industry can be regarded as bliss as it is a source of foreign exchange and royalty earnings. Tourism succors other industries like hotels, restaurants, handicrafts, and many more to run in an efficient way. Nepal Rastra Bank report shows total foreign currency exchange (less return) for 2018 stood at NRs. 69,750,584 thousand, (Around 617,263 thousand US$).
- Employment opportunities: Employment opportunities in the tourism and hospitality sectors can be created either directly or indirectly. Direct Employment opportunities are the total number of job opportunities supported directly by travel and tourism for instance guides, employment by hotels, restaurants, rural inns, and guest houses, museums, travel agencies, tourism information offices, protected areas such as national parks, palaces, religious sites, monuments, aircraft, photography, sightseeing tours, farmhouses, local transportation. Tourism and hospitality also support indirect employment in activities like restaurant suppliers, construction companies that build and maintain tourist facilities, as well as necessary infrastructure, various handicrafts producers, marketing agencies, accounting services.
- Cultural exchange: Tourists from various countries with different cultural backgrounds visit Nepal. In addition to that, Nepal is a home of people with unlike cultural frameworks from being multilingual to multiregional. Hence people can know each other more and learn about their language, art, skill, food, etc.
- Publicity of nation: Nepal is a small country and has not made a remarkable name in the world scenario. Tourism helps to publicize the country around the world so that more people know Nepal and its authentic beauty. It helps to publicize Nepalese art, skills, tradition, culture, and hospitality to the world.
Ecotourism in Nepal
Ecotourism is defined as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education” (TIES, 2015). It is about uniting conservation, communities, and sustainable travel. In the sixth plan (1980-1985 AD), emphasis was given to the promotion of eco-tourism in Nepal by the government. Since then ecotourism has been flourishing and attracting tourists towards Nepal for wildlife viewing, wilderness camping, trekking, hiking vacations, white water rafting, and many more activities. Along with the conservation of floras and faunas, national parks, conservation areas, wildlife reserves, and hunting reserves have been serving as a prime destination for tourists to enjoy jungle safari and watching wildlife closely. This is an example of ecotourism in Nepal. Moreover, except the main areas of Nepal that are easily accessible by the tourists like Kathmandu, Bhaktapur, Lalitpur, Chitwan, Pokhara, Lumbini, etc, rustic areas with abundant possibilities aiding to the attraction of tourists like Manang, Mustang, Dolakha, etc are being promoted for tourism.