Every civil engineering structure, whether it is a building, a bridge, or a dam, is founded on or below the surface of the earth. Foundations are required to transmit the load of the structure to the foundation soil safely & efficiently. Different types of foundations used in civil engineering constructions can be classified as follows:
Shallow Foundation
According to Terzaghi, a shallow foundation is one whose width is greater than its depth. i.e. Df/B<1. Such a foundation transmits the load to the upper strata of the earth & is generally provided to the lightweight structures. It is preferred when foundation soil has sufficient bearing capacity at shallow depth. When the sum of areas covered by each isolated footings is more than 50% of the total area of the foundation, mat foundation is adopted.
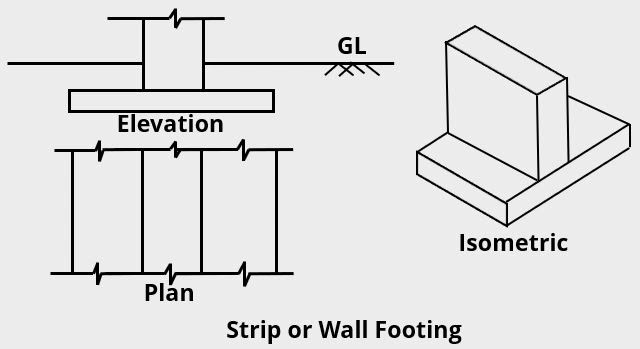
Strip or Wall Footing
Isolated or Spread Footing
Combined Footing
Strap or Cantilever Footing
Mat or Raft Foundation
Deep Foundation
A deep foundation is one whose width is less than its depth i.e. Df/B>1. Such a foundation transmits the load to the strata at a considerable depth below the surface of the earth & is provided to the heavyweight structure. It is preferred when the soil at the surface of the earth does not possess a considerable bearing capacity. The most common types of deep foundations are piles, piers & caissons. Well foundations are the special case of open caissons.