Methods of Soil Compaction | Types of Soil Compaction
- Tamper / Rammer
- Hand Operated Tamper
- Mechanical Tamper
- Roller
- Smooth Wheeled Roller
- Pneumatic Tyred Roller
- Sheep Foot Roller
- Vibrator
Types of Foundation Used in Civil Engineering Constructions
Shallow Foundation
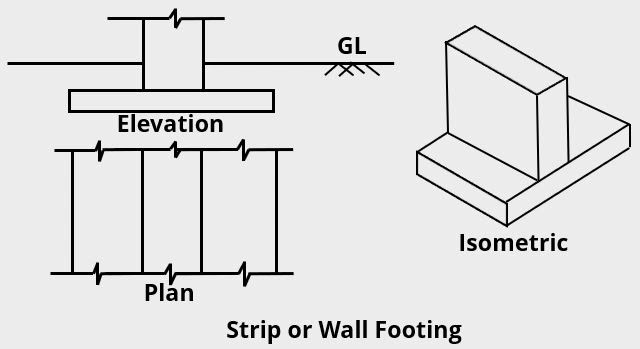
Strip or Wall Footing
Isolated or Spread Footing
Combined Footing
Strap or Cantilever Footing
Mat or Raft Foundation
Deep Foundation
What are the Criteria for Selection of Ideal Bridge Site?
Principles & Techniques of Bioengineering for Civil Engineers
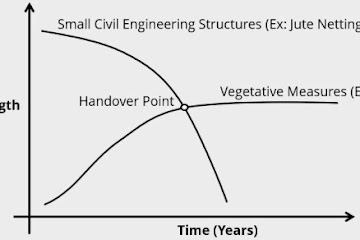
In a broader sense, Bioengineering is the use of life science & engineering to solve human life problems. Here, in this article, we are using the term bioengineering in the context of civil engineering & it basically refers to soil bioengineering. So, Bioengineering can be defined as the use of vegetative measures & small civil engineering structures in order to reduce the shallow seated instability. The living plants or non-living plant materials are used alone or in conjunction with small civil engineering structures for slope stabilization & erosion control. It utilizes locally available resources & is a cost-effective method.
Principles of Bioengineering
Functions of Bioengineering
- Catch
- Armor
- Reinforce
- Anchor
- Support
- Drain
Advantages of Bioengineering
- Immediate slope stabilization & erosion control
- Utilization of locally available resources (local tools, local manpower, local materials)
- It is a cost-effective method
- No need for frequent maintenance
- It also provides an opportunity for wildlife habitat
- It also improves the aesthetic beauty of the site
Commonly Used Techniques of Bioengineering
- Fascine: Bundle of live branches laid in shallow trenches
- Palisade: Woody cuttings planted across the slope.
- Wattling: Fence made out of vegetative materials.
- Bamboo Planting: Planting of bamboo for soil conservation
- Grass Planting: Planting of grass across the slope
- Brush Layering: Layers of woody cuttings planted in line following the contour
- RipRap: Stone pitching with vegetation interplanted between them
- Retaining Wall: Wall built to resist the pressure of earth filling or backing
- Toe Wall
- Breast Wall or Revetment Wall
- Check Dam: Dams constructed across the gullies to retard the flow
- Gabion Wall: Walls made up of gabion wire filled with stones
- Stone Masonry: Masonry construction using stones & mortar
- Jute Netting: Protecting the slope with standard jute mesh
- Rock Netting: Wire mesh of reliable material used to control the rockfall
- Rock Bolting: Reinforcement of rock slope by inserting steel bars
- French Drain: Subsurface drainage channel filled with aggregates
Degree of Static & Kinematic Indeterminacy of Structures
Parts of Research Paper | How to Write a Research Paper?
A research paper is scientific writing that shapes up an idea into words with solid and verifiable evidence. The main goal of a research paper is to assemble different opinions, perspectives, corroboration, and facts on a subject matter from various resources like articles, books, other research papers, interviews and elucidate the details and findings in one's own words. The most popular types of research papers are argumentative papers, analytical papers, definition papers, compare and contrast papers, cause and effect papers, reports, and interpretive papers.